What is it?
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) was founded in 1987 as a governmental agency with the objectives of:
- Creating consistent quality standards for a wide range of manufactured and agricultural products.
- Conducting product testing
- Ensures adherence to established standards.
- Grants licences for the official use of a designated mark, for meeting BIS quality standards.
The entity is recognized as the ‘National Standards Body of India’ overseen by the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution.

Features & Role of BIS
The BIS endeavours to enhance product development, protect the environment, mitigate health risks, and restrain the proliferation of goods.
The BIS is involved in carrying out the following roles:
- Enables the Government of India for BIS hallmarking schemes for precious metals which is necessary for certification.
- Enables any third-party agencies to certify and enforce the standards.
- Protects the interest of end users by providing certification and standardisation of products.
- Eliminates sub-standard products by mandating marking requirements.
- Facilitates third-party lab services for product testing.
- Formulates and implements standards for various products with the aid of relevant government departments.
- It provides facilities for repair of products which must bear standard marks.
- The Act has identified new areas for standardisation such as:
- Medical services
- Smart cities
- E-mobility
- New and renewable energy
- Digital technology
- Alternate fuels
Functions of BIS
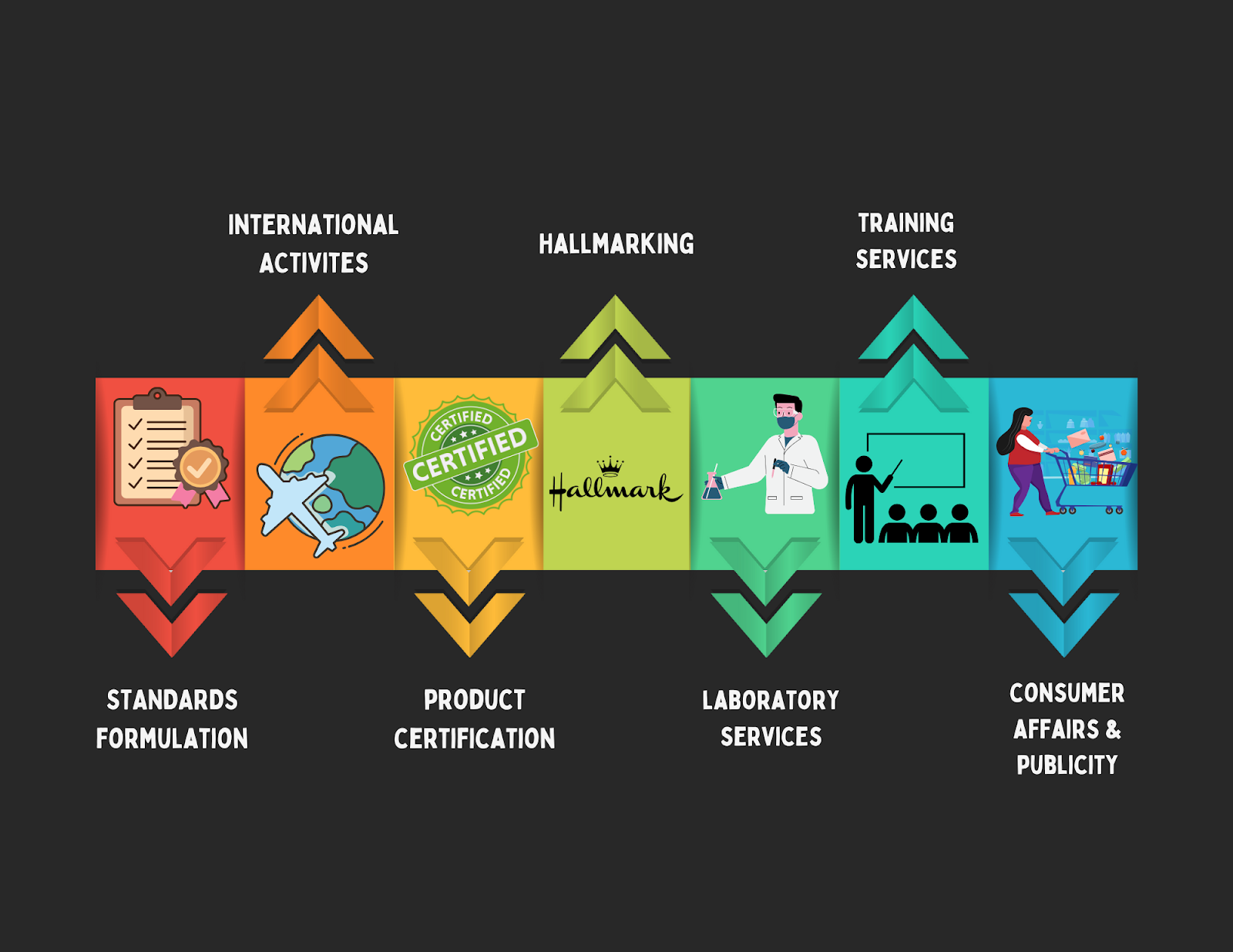
BIS operates across various domains, encompassing a range of activities aimed at fostering standardisation, marking, and quality certification of goods. The functions of BIS can be categorised into the following key areas to effectively oversee and facilitate these processes:
Standards formulation
The BIS is organised into diverse sectors, comprising 14 departments, where some of the major sectors include:
- Civil
- Chemicals
- Medical equipment
- Food and agriculture
- Transport Engineering
Each divisional council is further segmented to facilitate the enhancement of quality standards for their respective products and services.
Refer to the given link to know more about Standards Formulation- https://www.services.bis.gov.in/php/BIS_2.0/eBIS/
International activities
The following international organisations play a pivotal role in promoting standardisation, certification processes, and testing activities:
- International Organisation for Standardization
- Regional and Bilateral Cooperation
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Electro-technical Commission
Their active involvement is aimed at fostering growth and development across various industries.
Product certification
The BIS certification process is a compulsory procedure that manufacturers must adhere to when intending to market their products. This process must be completed before granting a licence to the manufacturer to:
- Ensure competence
- Verify the product conforms to established standards through testing.
Refer to the given link to know more about Product Certification- https://www.bis.gov.in/product-certification/
BIS Hallmarking
Hallmarking serves as a crucial purification and verification process for various articles like gold, platinum, silver and more. The primary goals of hallmarking are to:
- Safeguard the public from adulteration and uphold legal standards of fineness.
- Maintain product integrity by accurate determination during the purchase of an article.
Refer to the given link to know more about Hallmarking- https://www.bis.gov.in/hallmarking-overview/

Laboratory services
The BIS has set up several laboratories to guarantee that products available in the market meet the required standards for health and safety.
Refer to the given link to know more about Laboratory services- https://www.bis.gov.in/laboratorys/laboratory-services-overview/
Training services
The National Institute for Training for Standardization, established by BIS, aims to:
- Safeguard consumers through the training of technical and managerial personnel.
- Creation of consumer organisations and government undertakings to further enhance consumer protection
Refer to the given link to know more about Training services- https://www.bis.gov.in/training-2/overview-of-nits/
Consumer affairs & publicity
The following initiatives play a crucial role in certifying products for the audience and fostering awareness:
- Consumer awareness programs
- Industry awareness programs
- Managing public grievances and public relations
Refer to the given link to know more about Consumer affairs- https://www.bis.gov.in/consumer-overview/
BIS Registration
The mandatory BIS registration process is designed to certify products in accordance with Indian quality standards. The BIS mark serves as a prominent symbol of a product’s:
- Quality
- Safety
- Reliability
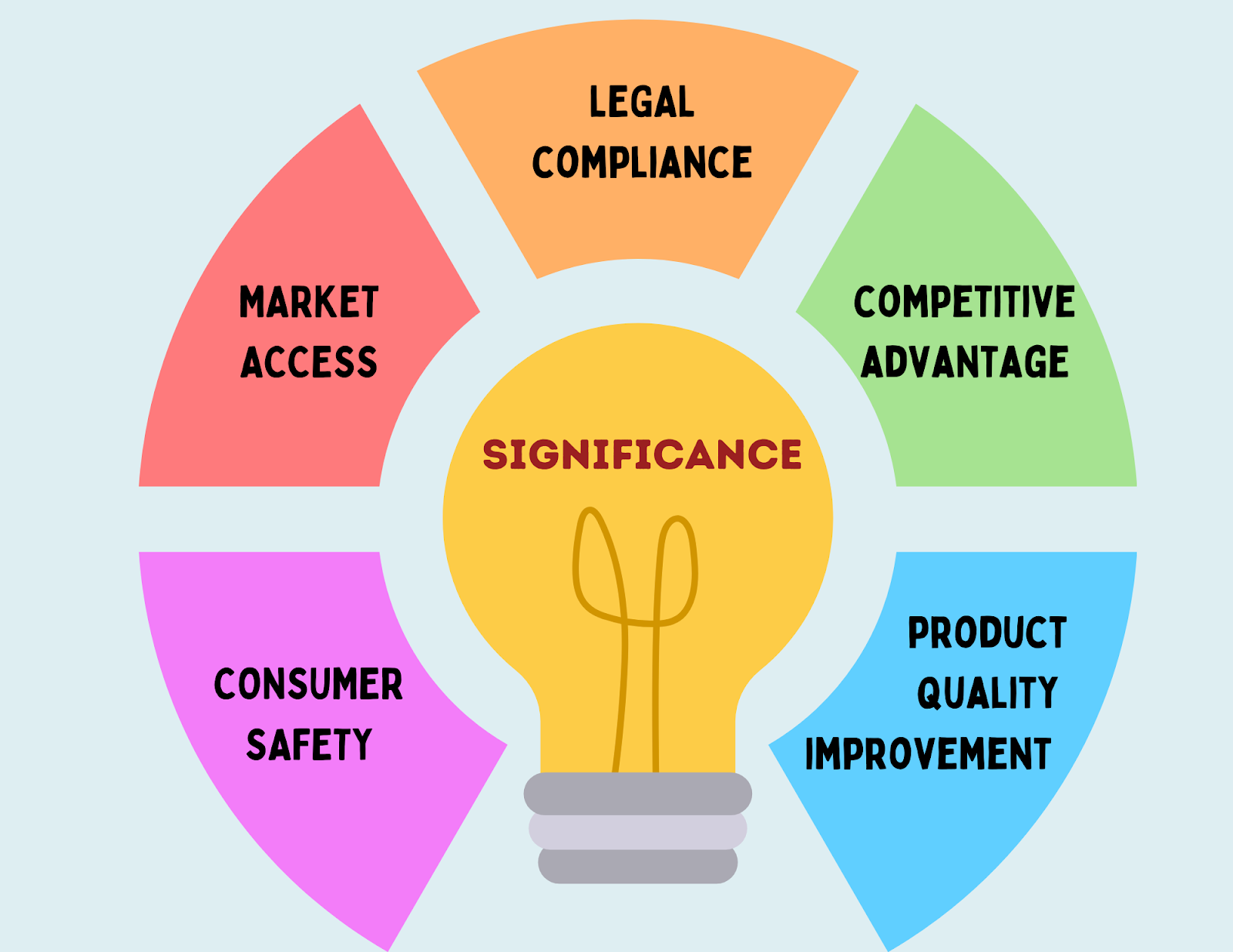
Significance of BIS registration
1. Consumer safety:
BIS Registration is a crucial step to ensure products comply with essential safety and quality standards, minimising the potential harm to consumers. This process plays a vital role in preventing the sale of inferior or potentially dangerous goods in the Indian market.
2. Market access:
Obtaining BIS certification is frequently mandatory for products intending to enter the Indian market. Without this certification, manufacturers could encounter limitations or even bans on selling their products in India.
3. Legal compliance:
Manufacturers must comply with BIS Registration, a mandatory legal requirement for numerous products in India. Failure to adhere to these regulations can lead to penalties and restrictions on market access, making it essential for successful operations in the country.
4. Competitive advantage:
In the Indian market, products with the BIS mark gain a competitive edge. Consumers favour and trust items featuring this symbol, as it indicates a commitment to quality and safety.
5. Product quality improvement:
The BIS Registration serves as a catalyst for manufacturers to enhance their product quality, leading to overall benefits for consumers. Adhering to BIS standards compels manufacturers to aim for improved product performance and safety, fostering a commitment to higher quality standards.
Products covered under BIS registration
BIS registration encompasses a diverse array of product categories, spanning, but not confined to:
- Electronics and Information Technology (IT) items
- Components for Automobiles
- Materials for Construction
- Chemicals and Petrochemicals
- Products in the Food and Agricultural sector
- Mechanical Engineering goods
- Medical Devices
- Safety Gear
- Textiles and Leather goods
- Toys
BIS registration process
The process of BIS registration generally encompasses the following stages:
- Submission of application: Manufacturers initiate the BIS certification process by submitting an application, including essential documentation like product specifications, test reports, and quality control plans.
- Sample Verification: Accredited laboratories under BIS carry out thorough testing on representative product samples to verify adherence to the applicable Indian standards.
- Facility Inspection: Representatives from BIS may conduct on-site visits to the manufacturer’s facility to evaluate the production processes and the implementation of quality control measures.
- Certification Approval: Upon successful verification of adherence to specified standards and quality requirements, BIS issues a certification, permitting the manufacturer to display the BIS mark on their products.
- Ongoing Oversight and Renewal: BIS maintains ongoing oversight through periodic surveillance and quality audits to ensure continued compliance with standards. Manufacturers are required to renew their certificates at regular intervals.

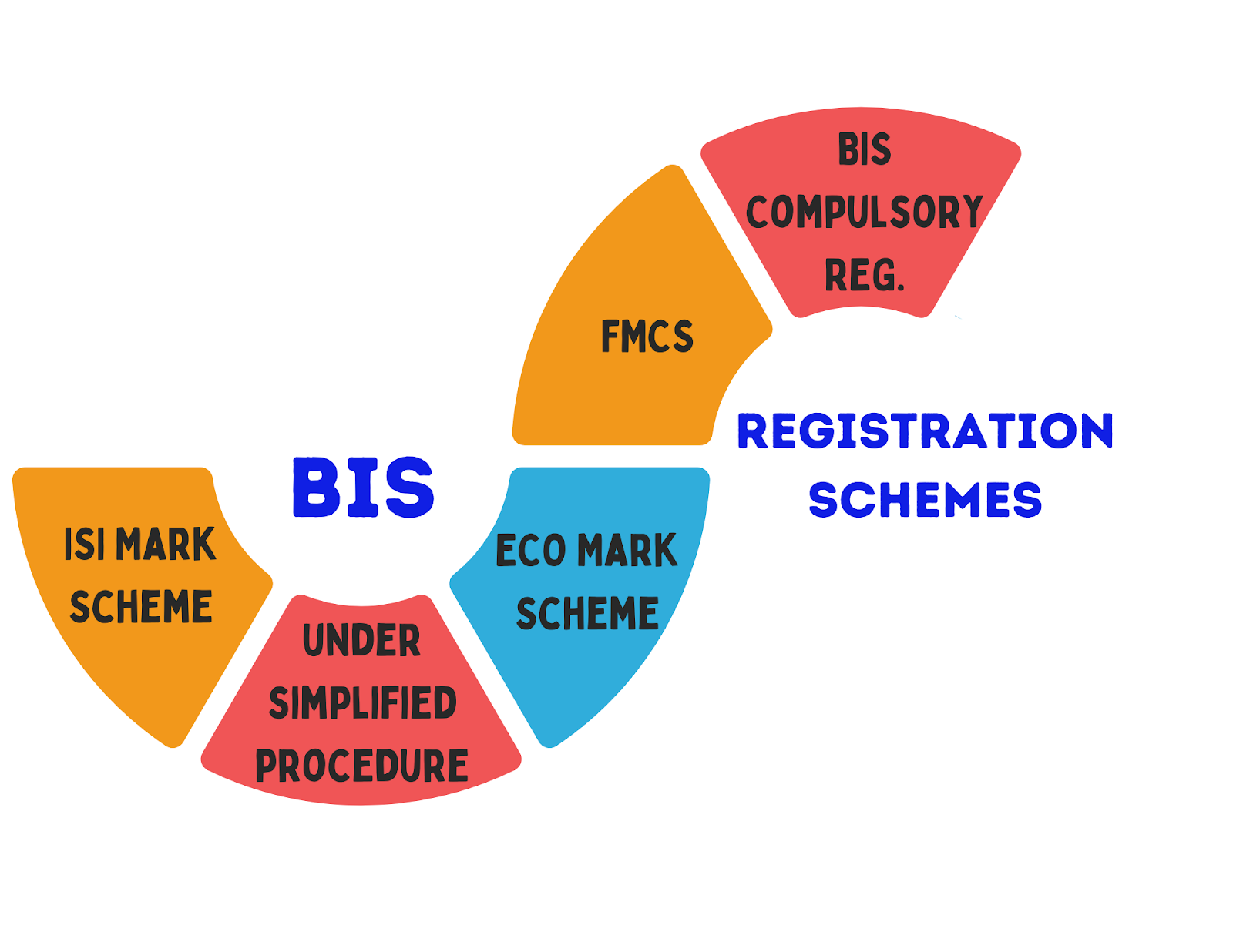
BIS Registration Schemes
BIS certification is granted through various schemes for different types of products, outlined as follows:
ISI Mark Scheme Registration
- Manufacturers of products subject to compulsory BIS certification (Scheme-I) must register through the standard procedure.
- Some mandatory certification products are also included in the list eligible for simplified registration.
- For products falling under both categories, manufacturers should opt for simplified registration rather than the regular procedure.
- In the standard BIS certification process, manufacturers submit the BIS registration application (Form V under Scheme-I) to the authorised officer in the manufacturing unit’s jurisdiction.
- The application is accompanied by necessary documents and fees.
- After receiving the application, BIS officers conduct a preliminary factory evaluation.
- Samples are collected and independently tested, generating a testing report.
- Once products meet quality standards, BIS certification/licence is granted.
The entire process takes 4-6 months from submitting the registration application.
Registration under simplified procedure
The BIS has introduced an expedited process to streamline BIS licence issuance. Manufacturers of products falling under the simplified procedure must compulsorily seek BIS certification:
- BIS licence approval is guaranteed within 30 days of submitting the simplified BIS certification application.
- Manufacturers need to submit the BIS registration application, requisite documents, self-assessment reports, and product sample test reports from an approved lab to the designated BIS officer.
- Upon meeting standard requirements in the test report, the BIS officer conducts a factory verification, leading to the issuance of the BIS certification within the stipulated 30-day timeframe.
The simplified procedure is not applicable in specific scenarios outlined below:
- Items such as valves, cylinders, cement, etc., require approval from relevant statutory bodies.
- For products granted a BIS licence based on factory testing, compliance is essential.
Refer to the consolidated guidelines on simplified procedure for grant of licence- https://bis.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Doc-7.pdf
ECO Mark Scheme
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) extends certification to environmentally friendly products through the ECO mark scheme:
- BIS issues an ‘ECO’ logo and an ‘ISI Mark’ to qualifying products.
- The dual logo and mark signify compliance with environmental criteria and Indian Standards quality.
- The process for obtaining a BIS licence under the ECO mark mirrors that for domestic manufacturers under standard or simplified registration.
- If a manufacturer possesses a valid BIS certification for a product and wishes to include a new product under the ECO mark, they must request the BIS.
Foreign Manufacturers Certification Scheme (FMCS)
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) facilitates the issuance of the ISI mark through the Foreign Manufacturers Certification Scheme (FMCS) for international applicants or foreign manufacturers, completing the process within six months. This certification applies to:
- Products falling under the Compulsory Registration Scheme (CRS)
- Mandatory BIS certification scheme (Scheme-I).
- FMCS allows overseas entities to secure and display the standard ISI mark on their products. To avail this, foreign manufacturers must establish a branch office in India, fulfilling the requisite formalities, and appoint a representative based in India.
BIS Compulsory Registration Schemes
The BIS issues licences to manufacturers of electronic products, allowing them to use the standard mark with a unique R-number.
- To obtain BIS certification under the CRS, manufacturers can register through a self-declaration of conformity for each product by filing Form-I under smart registration.
- Manufacturers must procure test reports for their products from BIS-recognized laboratories. These verified test reports should be submitted to the BIS along with an undertaking of conformity for the product.
- If the application submitted by the manufacturer indicates that they possess the necessary infrastructure for consistently producing quality products, the BIS will grant BIS certification under the CRS.
Bureau of Indian Standards, 2016
In 2016, the Bureau of Indian Standards Act replaced and superseded the 1986 Bureau of Indian Standards Act, with the primary objective of instituting a national standards body:
- The BIS Act of 2016 gave rise to the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) as the official National Standards Body for India.
- This legislation established a dedicated Bureau specifically tasked with standardising products and processes, along with implementing marking and certification procedures.
- The BIS Act proposed an expansion of its influence by empowering the central government to mandate the use of the standard mark for specific items, commodities, processes, and other relevant matters.
Refer to the Act from the Official Gazette- https://bis.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/BIS-Act-2016-Bilingual.pdf
Provisions of the Act
- The Act empowers the central government to mandate the inclusion of standard marks on specified goods, processes, articles, etc., in the interest of the public, environmental safety, national security, or to prevent unfair trade practices.
- The Act authorises the central government to designate agencies or authorities (in addition to BIS) for verifying product and service conformity and issuing conformity certificates.
- The Act incorporates provisions for the recall or repair of products bearing the Standard Mark but failing to meet the required Indian standard.
- The Act identifies new domains for standardisation, encompassing Medical devices, Alternate fuels, Smart cities, E-mobility, New and renewable energy, and Digital technologies (Artificial Intelligence, Industry 4.0, Blockchain, etc.).
- Violating the use of the Indian standard mark can lead to a penalty of up to Rs. 5 lakh.
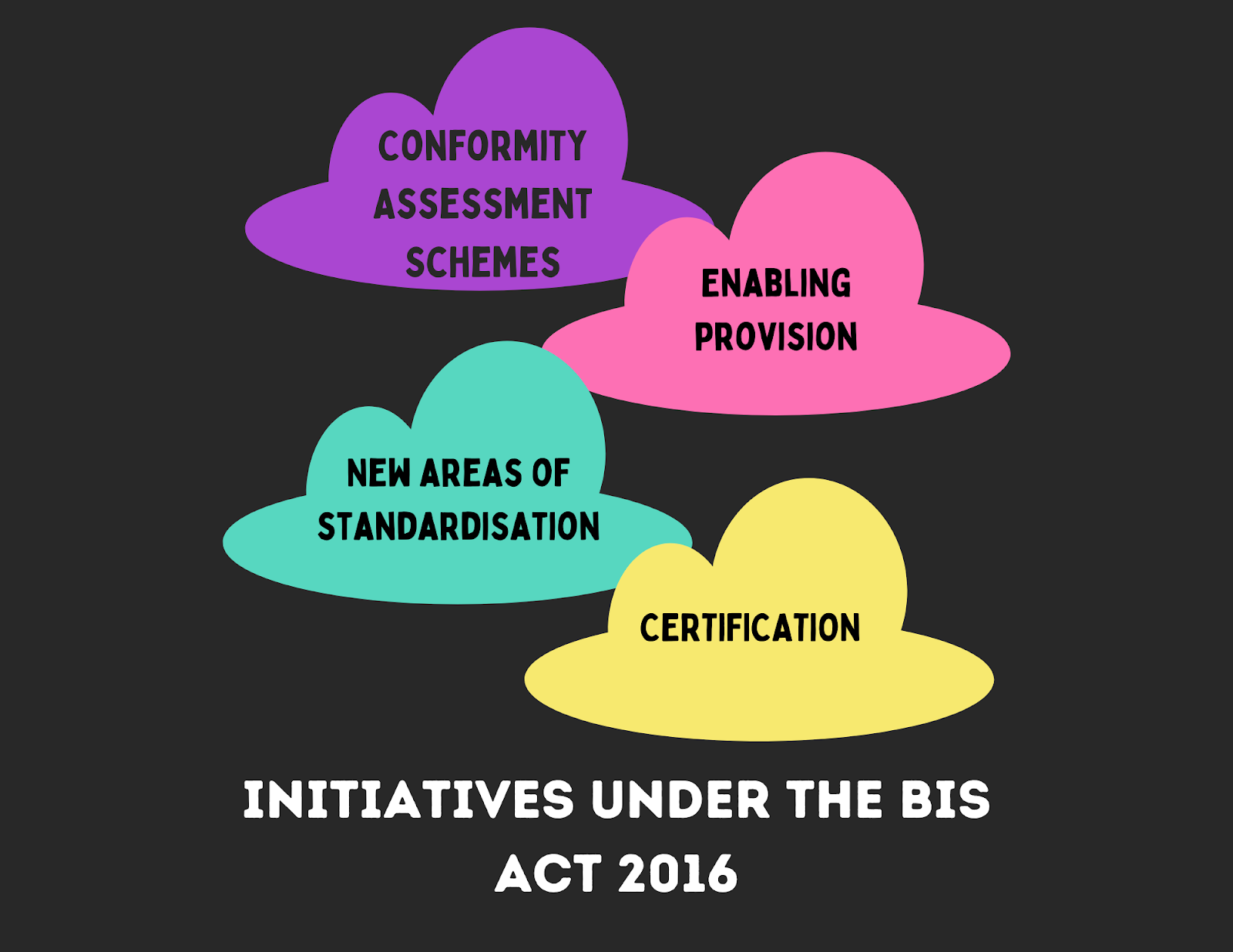
Initiatives of the BIS Act, 2016
1. Conformity Assessment Schemes:
The 2016 Bureau of Indian Standards Act enables easier conformity assessments, allowing producers flexibility through options like self-declaration for compliance.
2. Enabling provision:
The 2016 Bureau of Indian Standards Act empowers the government to mandate certification for goods or articles from scheduled industries, processes, systems, or services, deemed essential for public interest, safeguarding human, animal, or plant health, or ensuring national security.
3. New areas of standardisation:
The BIS Act of 2016 introduces novel domains within the realm of standardisation, encompassing:
- Alternative fuel
- Electric mobility
- Medical devices
- Smart cities
- Digital technologies (Industry 4.0, Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain, etc.)
- Emerging and renewable energy sources.
4. Certification:
Certification marks found on commercial goods often serve as indicators of authenticity or assurance, signifying that the manufacturer has thoroughly examined the product and verified its adherence to prescribed quality standards.
BIS Services by JPARKS INDIA
Join hands with JPARKS INDIA for BIS certification excellence! Elevate your products with quality assurance and gain a competitive edge in the market. Enquire today!
Why choose JPARKS INDIA for your BIS certification?
- Expertise- Team of professionals with extensive industry knowledge who guides you through every step, leaving no room for compromise.
- Precision- We navigate the complexities of BIS certification with finesse, and your products undergo rigorous scrutiny to adhere to the BIS standards.
- Unwavering integrity- We ensure that your products meet not only regulatory standards but also build trust among your consumers.
- Speedy market access- Time is of essence in today’s fast-paced business environment. JPARKS INDIA accelerates your access to the market without compromising the quality of certification.
Connect with JPARKS INDIA to be your very own catalyst for BIS certification services!
Apply for BIS marks I FAQs
What is the purpose of BIS?
The primary objective of BIS is to foster the coordinated advancement of standardisation, marking, and quality certification processes for goods.
What is the difference between ISO and BIS?
ISO functions globally, establishing and endorsing standards across industries. Meanwhile, BIS operates nationally, focusing on setting standards specific to India’s industries and sectors.
Is BIS mandatory in India?
While the BIS certification scheme is generally voluntary, the Central Government mandates compliance with Indian Standards for certain
What are BIS quality standards?
The BIS Standard Mark on a product signifies its adherence to Indian Standard Specifications, assuring consumers of quality, safety, and reliability. BIS Conformity Assessment Schemes instil confidence in consumers, ensuring effective consumer protection.
What are ISI standards?
Since 1950, the ISI mark has served as a certification for industrial products in India, indicating compliance with Indian standards established by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), the country’s national standards organisation.
How can I get a BIS certification in India?
To secure a BIS licence, manufacturers must possess the necessary production facilities, implement suitable process controls, and maintain quality assurance and testing capabilities aligned with the relevant Indian Standard (ISS).
What is the BIS logo on products?
The Bureau of Indian Standards requires the affixing of the BIS Logo on both the product and its packaging once the BIS Registration Number for that particular product has been obtained.
What is the BIS law in India?
The Bureau of Indian Standards Act of 2016 established the BIS in India.
What is the BIS approved symbol?
Once you obtain the BIS certificate, you have the option to affix either the hallmark logo or the BIS-ISI logo on your product.
Where can I find an agent to help me obtain a BIS certification?
JPARKS INDIA Pvt. Ltd. specialises in obtaining both Preferential and Non-Preferential CoOs within a span of 1-2 days at the most affordable rates. You can look us up on Google as well as our website to know more about our services.








